After harvesting coconuts from the trees, the outer husk surrounding the nut is removed. It is called de husking.
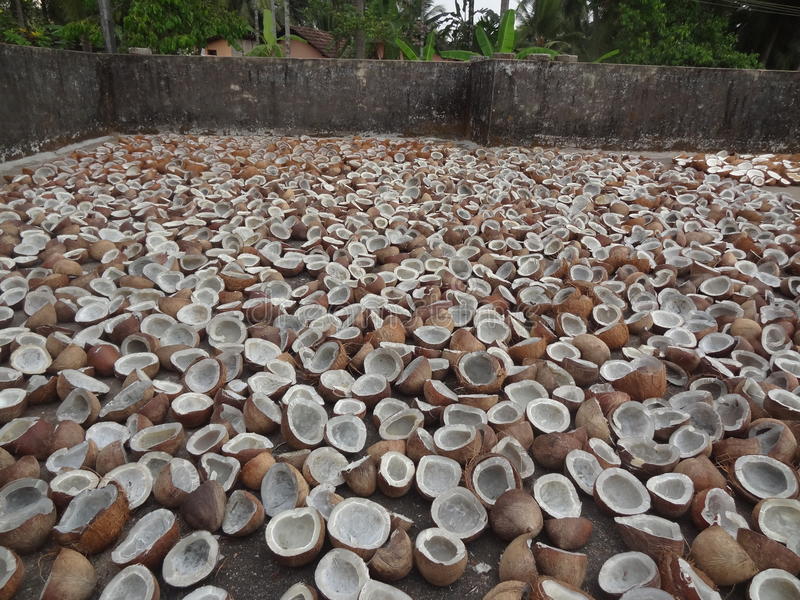
Then we get the nut into our hands. Again the hard shell of the nut is cracked and de shelled. Finally we have the coconut flesh.
Then the coconut flesh is stripped and chopped into small pieces and put out to sun dry for eight days. Normally coconut flesh pieces are put out on a polythene on ground. If there is rain and coconuts get wet and again dried randomly, then final copra will be contaminated with fungi. Sun drying can cause downfall in quality due to dirt and dust on ground and air.
You will need 5 coconuts to produce 1kg of copra (i.e. sun drying of the flesh of 5 coconuts will give you 1kg of copra), which can be used to press oil out of it. And roughly 1.6kg to 2.0kg of copra is needed to produce 1 liter of coconut oil.
When copra having fungi are used to press coconut oil, in the final coconut oil product there shall be aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
When sun drying is over and copra is obtained, the bulk copra is put inside an Anderson type hot press expeller which is mass scale and high output, when compared to virgin coconut oil cold press expelling machines. A virgin coconut oil expeller machine can produce around 500 liters of virgin coconut oil per day. But a hot press conventional expeller can produce 5000 liters of normal coconut oil per day.
That is the difference in pressure applied and speed of pressing when comparing cold press machine and a hot press machine.